What’s the Difference Between Data Analytics and Data Science?
- 13 Mar 2023
- 6 min read
Data Analytics and Data Science are two distinct fields that help companies understand big data. While both involve working with large datasets to uncover patterns and make informed decisions, there are significant differences between the two. In this article, we will explore those key differences to help you choose the right career for you.

Data Analytics vs. Data Science – What’s the Difference?
You might notice that the terms “data analytics” and “data science” are often used interchangeably. This can create confusion, but there are key distinctions between the two disciplines that are important to understand.
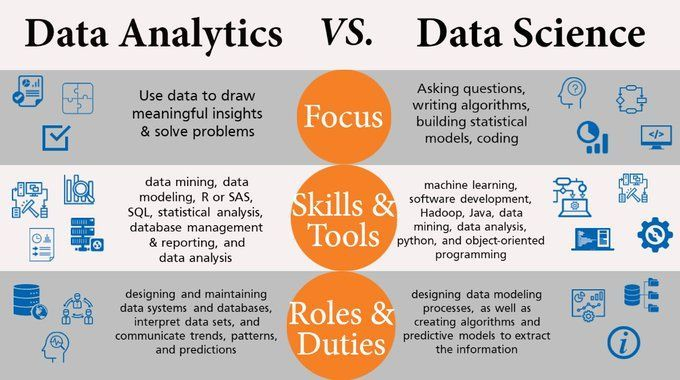
Data analytics refers to the process of examining large datasets to uncover patterns or notice trends. The main purpose of a data analyst is to find correlations between different sets of data. This helps them make predictions about future outcomes based on what has happened in the past.
The goal of data analytics is to gain insights on how some processes can be optimised for maximum efficiency and effectiveness in the future.
Data science, on the other hand, goes beyond simply analysing existing datasets. Data scientists will develop algorithms and models that can help extract information from data sets in order to find actionable insights. They attempt to predict potential trends based on data they’ve collected, explore disparate and disconnected data sources, and find better ways to analyse information.
The goal of data science is to ask questions and locate potential avenues of study with less concern for specific answers and more emphasis on finding the right questions to ask.
In summary, both disciplines work with big data, but the big difference lies in what they do with that data. Data analysts examine large data sets to identify trends, develop charts, and create visualisations that help businesses make more strategic decisions. Data scientists develop new processes for data modelling and production using prototypes, algorithms, and predictive models to try and determine what might happen in the future.
What Does a Data Analyst Do?

Broadly speaking, data analysts use data to solve problems by identifying patterns, trends, and insights.
Using a variety of tools and techniques, they analyse datasets in an attempt to explain why sales dropped in a certain quarter, to determine the success of a marketing campaign, or to show how staffing changes impact revenue. By answering these questions, they can provide insights to their organisation. These are just a few ways they apply data to help businesses grow and succeed.
In practice, data analysts come in many different forms. There are plenty of ways you can specialise as a data analyst depending on your interests and skills. Some of these include:
- Database analysts
- Business analysts
- Market research analysts
- Sales analysts
- Financial analysts
- Marketing analysts
- Advertising analysts
A successful data analyst possesses both the technical ability to do their job well and the communication skills to relay the information gathered to people with a less technical background. These technical skills include data mining, data modelling, and database management & reporting. Typically, data analysts will use statistical analysis systems (SAS) and the statistical programming language, R, to perform these analyses.
The daily life of a data analyst might consist of designing and maintaining data systems or databases, using statistical tools to analyse datasets, or presenting reports on their findings to relay information about trends, patterns, and predictions that come from that data.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?

Data scientists take analytics one step further. In general, they make educated guesses about the unknown by asking probing questions, designing predictive algorithms, and developing new statistical models. A data scientist possesses a deep understanding of mathematics and statistics, knows how computers work, and has substantive experience.
A big distinction that sets data science apart is its reliance on extensive coding. Data scientists have the skills to use several statistical and analytical tools to arrange and analyse undefined data sets at the same time. Importantly, they also know how to construct their own automation systems and frameworks by writing algorithms or programming machinery.
Data scientists use these skills to help businesses predict trends, direct potential areas of research and development, and find better ways to analyse information.
In practice, data scientists come in many different forms. There are plenty of ways you can specialise as a data scientist depending on your interests and skills. Some of these include:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
- Database Administrator
- Data Architect
- Data Engineer
- Software Engineer
- Statistician
Often, data scientists are busy constructing algorithms and predictive models and designing data modelling methods in order to provide valuable insights and outlooks for a company’s future.
A data scientist’s job is typically a bit more specialised. It will require a deep understanding of complex coding languages like Java and Python, as well as proficiency in using data storage tools like Hadoop. Alongside this knowledge, data scientists do data analysis and software development, and understand how to use machine learning to get results.
Is Data Analytics or Data Science Right For Me?
In today’s job market, employers are constantly looking for qualified candidates to fill data-focused positions. All companies create data and there is a strong incentive for them to find someone who can make sense of – and use – that data.
Importantly, there are major differences between data analysts and data scientists, despite their deceptively similar job titles. The educational requirements, job responsibilities, and career trajectories are very different – it’s important to know this before choosing a career in either.
In short, both disciplines involve working with complex sets of information. Data analytics focuses primarily on discovering relationships and patterns within existing datasets. Data science employs sophisticated tools like machine learning algorithms to draw conclusions from these relationships and make predictions about the future.
If you have an eye for detail and a knack for picking up trends and patterns, data analytics might be the career choice for you. On the other hand, if you’re into coding, are good at maths, and like to speculate about what might happen in the future, data science might be right for you. No matter which you choose, ALX offers courses for each that will prepare you to enter the job market as a strong and capable candidate.
Ultimately, each field has its own set of advantages, depending on the problem that needs to be solved. So long as you consider your background, personal interests, and skills, you can choose the career that is the best fit for you on your journey to success.
Start your journey today by enrolling in the ALX Data Analytics programme or the ALX Data Science programme. Our courses are delivered in a ‘practical, hands-on, roll-up-your-sleeves and get stuff done’ manner, in partnership with ExploreAI.
